In this blog, I will discuss why this is exactly happening with the Indian unemployment rate and try to give a few good solutions for it. Hopefully, this blog will reach someone responsible enough and will make a net positive impact.
Where does the unemployment rate of India stand right now?
As of March 2024, the unemployment rate in India has decreased to 7.6%. We are showing a slight drop from 8% in February 2024 (Study IQ Education). This decline has been observed in both urban and rural areas, with urban unemployment at 8.2% and rural at 7.4% for March (Adda247).
Unemployment rate and education
Right now if someone is a graduate he is 9% more likely to be unemployed.
I will just give some points as to why it’s a concerning case
- Mismatch of Skills: One primary concern is the mismatch between the skills graduates acquire in higher education and the skills demanded by employers in the job market. This mismatch can result from outdated curricula that do not align with current industry needs, leading to graduates who are not job-ready upon finishing their education.
- Economic Waste: High unemployment rates among graduates represent a significant economic waste. It means that the substantial investment in higher education—both from the individuals and the government—does not yield the expected return in terms of productive employment and economic contributions.
- Underemployment: Graduates who do find employment often end up in jobs that do not require a degree. This underemployment not only wastes their skills but also leads to dissatisfaction and lower wages than those associated with degree-requisite jobs.
- Social and Psychological Impact: Long-term unemployment or underemployment among graduates can lead to psychological distress, lowered self-esteem, and a pervasive sense of underachievement. It can also lead to social unrest, particularly when large numbers of young people feel disenfranchised and disconnected from economic opportunities.
- Economic Growth and Innovation Stagnation: Economies benefit from the innovative ideas and increased productivity that higher education graduates can provide. High unemployment rates among these individuals can slow down innovation and economic growth, affecting the country’s competitive edge in the global market.
What is unemployment?
Unemployment refers to the condition of someone actively searching for employment but unable to find work.
and what are the types of unemployment?
- Frictional Unemployment: This occurs when there is a temporary disconnect between jobs and workers. It includes people who are switching jobs, entering the workforce for the first time, or re-entering the workforce after a break. It’s generally short-term and a natural part of a dynamic economy.
- Structural Unemployment: This results from a deeper, more permanent mismatch between the skills workers can offer and what employers need. It can be due to technological changes, where new skills are required, or industries declining because of shifts in the economy.
- Cyclical Unemployment: Linked to the economic cycle, this type of unemployment increases during recessions and decreases during periods of economic growth. It reflects a general lack of demand for goods and services, which leads to job cuts.
- Seasonal Unemployment: Some industries, like agriculture or tourism, are seasonal, meaning the demand for labour goes up and down depending on the time of year. Workers in these sectors might be unemployed during off-season periods.
- Long-term Unemployment: This refers to individuals who have been unemployed for an extended period, typically 27 weeks or more. This can be particularly damaging as it erodes skills and makes it harder to be employed again.
The main reason I stated all these types is because in India we are seeing one of the most powerful types of unemployment – Structural Unemployment.
How are we seeing Structural Unemployment in India?
We can see Structural Unemployment in India for many reasons one of them being recent advancements in technology.
With Google’s transformer model and advancement in LLM (large language model) technology, we got to see products like chatGPT and others that pose a lot of risk in the job market, especially to people who are not up-to-date.
Another reason is Educational Mismatch. This is mainly because of layoffs in big companies like Google, Microsoft, Apple, etc. Right now the job market is flooded with highly technical individuals who want jobs. Hence The youth in India have to compete with highly technical and experienced candidates. By logic, young individuals will lose this race.
India has presently shifted from agriculture to the manufacturing and services industry and we can see this also as a contributing factor to Structural Unemployment.
How is unemployment calculated in India?
Not many people know about the National Statistical Office which operates under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. Now what do they do – they collect data and do a whole bunch of surveys and try to find out about various socio-economic aspects of the country.
The unemployment rate in India is calculated by the National Statistical Office first the N.S.O conducts something known as the Periodic Labour Force Survey, which is a key part of it.
To understand how unemployment is calculated in India we have to understand Periodic Labour Force Survey.
Rotational panel sampling design.
A rotational panel sampling design is a method of collecting panel data from the same sample of units over a specified number of measurement periods.
In our case, N.S.O. uses a rotational panel sampling design for the Periodic Labour Force Survey. Which just means different parts of the country are surveyed at different times. The survey collects data every quarter for urban areas and annually for both urban and rural areas.
Then they extract a lot of data like working for pay, profit, family gain, etc; but it’s outside of this blog scope so we won’t discuss that.
Last we come to the formula, which is:
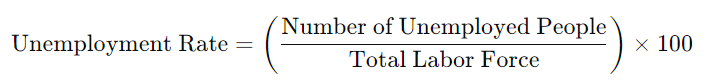
Yep, that’s it. Cause of all the problems 😂.
Now let’s talk about Reasons.
What many people do not know and understand is India’s economy has seen a structural transformation, with a shift from the primary sector to the tertiary sector. This means that the country’s reliance on agriculture is gradually decreasing, while the industrial and service sectors’ share of the total GDP is increasing.
Hate to say it, Now you know the stuff with farmers a little better.
- So a lot of the workforce was aligned with the education of the agriculture industry, this reformation will take 6 to 7 years to reflect on our current job market, but this factor is not very permanent.
- Another reason is the size of the population I don’t think I need to elaborate on this.
- Because of poor finance, poor markets, and low buying power in India, small ventures have become more difficult.
- Low investment in the manufacturing sector and inadequate infrastructure development.
Now let’s talk about the solutions to this.
Haha if I knew the solution to this problem I would be a secretary, not a stupid engineer. But as promised, I am going to give some solutions to you.
Government Job 😐
This thing was pointed out by one of my friends Gaurav. So why things are the way they are night now is best explained by giving an example, let me give you one.
Suppose two government departments X and Y.
X has a vacancy of 90 people and Y has a vacancy of 10 people. So what is traditionally done is that Y is ignored by the government officials and X is promoted and this shit piles up.
Over 60 Lakh Central and State Govt Posts Lying Vacant
SOURCE
The Indian government has over 40 lakh sanctioned posts, with more than 30 lakh employees and over 9.64 lakh posts currently vacant. This information was revealed in the Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha during the monsoon session of 2023.
Individual Growth
As now India has shifted to the industrial and service sectors, we as individuals need to understand that we are not married to technology or profession. We have to move, run and jump with the job market. We as individuals need to make ourselves useful to the world.
Is this the fault of the current government? No, not really. Is it the responsibility of the government to fix it? ABSOLUTELY YES!
What Government can do to Fix this
By creating industrial norms like ‘X’ size of the company, It has to employ ‘n’ number of young individuals. As we see more unemployment in Youth.
The government can establish workshops and certification programs to help young individuals.
Lastly, I think that the government should promote online learning and then take offline exams, which will quite drastically remove the skill gap made because of structural transformation.
Conclusion
Alright, wrapping this up before we all decide to run for government jobs! We’ve seen a small dip in the unemployment rate, which is kind of like finally hitting a four after a string of ducks. But hey, it’s not all cheers and applause yet.
We’re dealing with a beast called structural unemployment, which is sneakier than a spinner on a turning pitch. Add to that the mismatch of our educational cannonballs not hitting the industry’s battleship, and you’ve got a bit of a spectacle. The need of the hour? A solid team strategy where the government, educational maestros, and we, the hustling individuals, play together to hit those sixes.
So, let’s lace up, gear up, and show up, because if we don’t, who will? Let’s make employment not just a dream but a well-played reality. And remember, if none of this works, there’s always the allure of becoming a meme creator—seems like they’re always in demand!

Leave a Reply